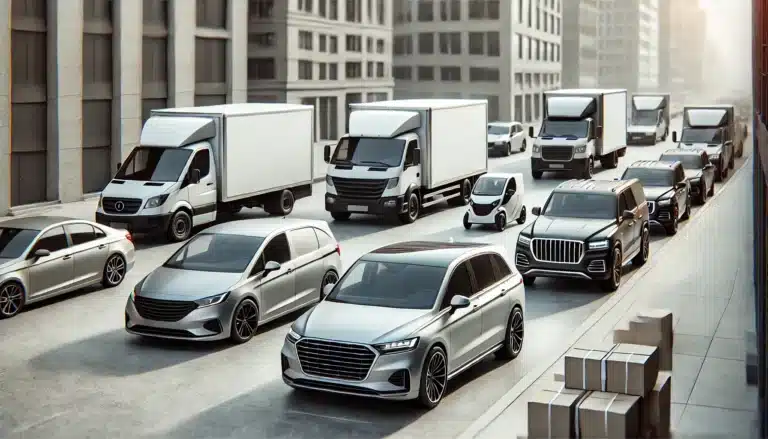
How Do I Insure My Business Vehicles? A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
How Do I Insure My Business Vehicles? Insuring your business vehicles is more than just a requirement; it’s a critical step in protecting your business from financial risks associated with accidents, damages, and liability claims. Whether you’re a small business owner or manage a large fleet, having the right commercial auto insurance is essential to ensure both compliance and peace of mind.
This guide will help you understand the essentials of business vehicle insurance, coverage options, and how to get started.
Key Takeaways: Insuring Business Vehicles
1. Separate Policy Is Essential
- A commercial auto insurance policy is mandatory for business vehicles, as personal policies exclude business use.
- Businesses using personal vehicles for work (e.g., deliveries or transporting tools) should consider Hired and Non-Owned Auto Insurance (HNOA).
- This coverage ensures both compliance with state laws and protection against unexpected risks.
2. Comprehensive Coverage Options
- Liability Insurance: Protects against third-party injuries or damages caused by business vehicles.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Shields vehicles from theft, vandalism, and weather-related damages.
- Collision Coverage: Covers repair or replacement costs for vehicles involved in crashes, regardless of fault.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: Pays for damages caused by drivers with insufficient or no insurance.
- Add-Ons: Towing, rental reimbursement, and roadside assistance offer additional convenience and protection.
3. Factors Influencing Insurance Costs
- Vehicle Type: Trucks, vans, and specialty vehicles typically have higher premiums than passenger cars.
- Driving History: Clean records lower premiums, while claims or violations increase costs.
- Coverage Limits: Higher limits provide better protection but raise premiums.
- Business Use: High-risk activities like deliveries or equipment transport may lead to increased premiums.
4. Essential Steps to Obtain Coverage
- Assess Needs: Identify the vehicles and employees requiring coverage based on business activities.
- Gather Information: Provide vehicle details (e.g., VIN, make, and model) and driver histories for an accurate quote.
- Compare Policies: Shop around and bundle policies for discounts.
- Review Regularly: Update coverage as your business grows or operations change.
What Is Business Vehicle Insurance?
Business vehicle insurance, often called a Business Auto Policy (BAP) or Commercial Auto Insurance, provides liability and physical damage coverage for vehicles used for business purposes. Unlike personal auto insurance, a BAP is tailored to meet the higher risk profile of vehicles used for work-related tasks.
Key Features of a Business Auto Policy:
- Covers vehicles owned, leased, or hired by a business.
- Protects against third-party liability claims and property damage.
- Includes optional add-ons for broader protection, such as collision, comprehensive, and uninsured motorist coverage.
Who Needs Business Vehicle Insurance?
Considering getting Business Vehicle Insurance? You’ll need commercial vehicle insurance if:
- Your business owns or leases vehicles.
- Employees drive personal vehicles for work purposes (e.g., deliveries or client visits).
- Your business relies on vehicles for transporting goods, tools, or equipment.
Cost for $100,000 Renters Insurance
-
For a policy with $100,000 in personal property and liability coverage, the average annual cost is about $426/year, which works out to roughly $36/month.
So in practice, the typical monthly range is $20–$35/month only if specific credits or discounts apply—but generally, it’s closer to $36/month under standard assumptions.
Differences Between Personal and Business Auto Insurance
| Feature | Personal Auto Insurance | Business Auto Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Who It Covers | You and immediate family members | Employees and authorized drivers |
| Use Case | Personal use, commuting | Business-related tasks, such as deliveries |
| Vehicle Types | Cars, vans, and SUVs for private use | Company cars, trucks, vans, and specialty vehicles |
| Liability Limits | Lower limits, suitable for personal needs | Higher limits, protecting business assets |
Coverage Options for Business Vehicle Insurance
- Liability Insurance: Covers third-party injuries and property damage caused by your business vehicle.
- Collision Insurance: Pays for damages to your vehicle in a crash, regardless of fault.
- Comprehensive Insurance: Protects against non-collision events like theft, vandalism, or natural disasters.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: Pays for damages caused by a driver who lacks sufficient insurance.
- Medical Payments (PIP): Covers medical expenses for drivers and passengers, regardless of fault.
- Add-Ons:
- Towing and roadside assistance.
- Rental reimbursement during vehicle repairs.
- Hired and non-owned auto insurance (HNOA) for personal vehicles used for work.
Which Companies Offer the Cheapest Renters Insurance in Texas?
-
Texas’s cheapest insurers (by average monthly/annual cost):
-
Allstate:
$20/month ($243/year) -
State Farm:
$24/month ($294/year) -
Nationwide:
$25/month ($305/year)
-
-
Per-city rates in Houston specifically:
-
Progressive: around $18/month (~$218/year) — the lowest among major insurers in Houston.
-
-
National-level comparisons:
-
USAA (exclusive to military community): among the lowest, but not accessible to everyone
-
State Farm: often cited as the least expensive for general availability — e.g., $195/year nationally.
-
Therefore, while Lemonade may offer affordable starting plans (e.g., $5/month for minimal coverage) Lemonade, in Texas specifically, Allstate, State Farm, Nationwide, Progressive, and USAA (if eligible) are among the most competitively priced.
How to Get Business Vehicle Insurance
- Assess Your Needs:
- Determine which vehicles and drivers require coverage.
- Understand your risk profile and coverage limits.
- Gather Necessary Information:
- Vehicle details: Make, model, year, and VIN.
- Driver details: License numbers and driving history.
- Annual mileage and vehicle use.
- Compare Quotes:
- Obtain quotes from multiple providers to find the best rates and coverage.
- Consider bundling policies (e.g., general liability and commercial auto) for discounts.
- Customize Your Policy:
- Choose coverage options based on your business operations.
- Discuss add-ons like HNOA or collision for comprehensive protection.
Conclusion
How Do I Insure My Business Vehicles? Insuring your business vehicles is a critical investment in your company’s future. From safeguarding against liability risks to ensuring compliance with state laws, a well-structured business auto policy can save you from unexpected financial burdens. Assess your needs, explore coverage options, and consult a trusted insurance provider to secure the right policy for your business. With the right coverage in place, you can focus on growing your business with confidence.
For tailored solutions, contact our insurance experts today for a customized policy review.